Complex-centric proteome profiling by SEC-SWATH-MS
Proteins are major effectors of biological processes and their organization into macromolecular complexes is of great biological and clinical significance. A recent “Molecular Systems Biology” paper by the Aebersold group (IMSB) presents a workflow for the parallel detection of hundreds of protein complexes and their variants in a single operation.
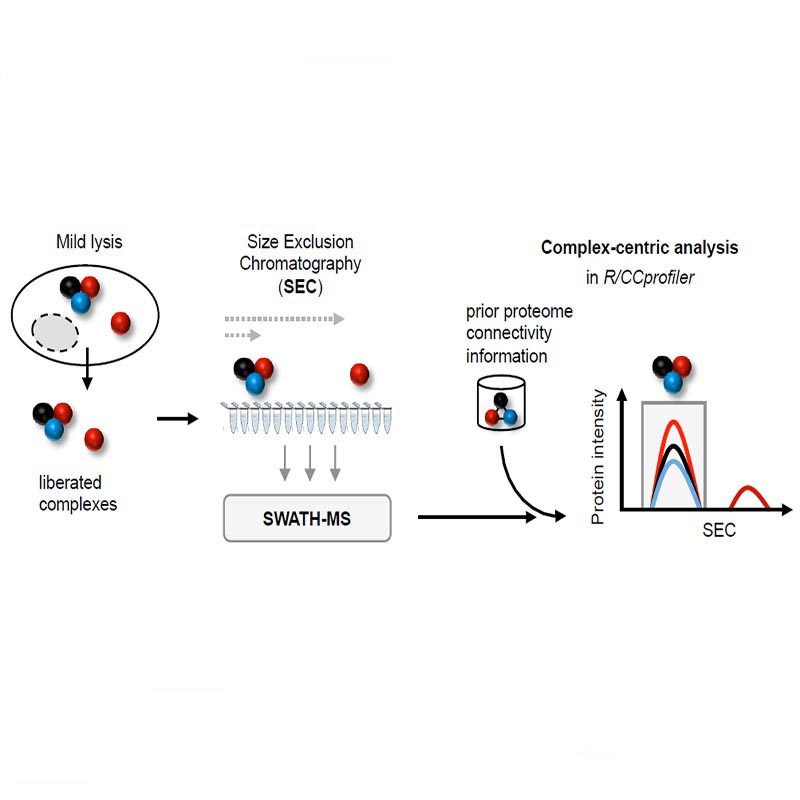
In their paper, the Aebersold group describes an integrated experimental and computational technique that consists of size exclusion chromatography (SEC) to fractionate native protein complexes, SWATH/DIA mass spectrometry to precisely quantify the proteins in each SEC fraction, and the computational framework CCprofiler (external page https://github.com/CCprofiler/CCprofiler) to detect and quantify protein complexes by error‐controlled, complex‐centric analysis using prior information from generic protein interaction maps. Their analysis of the HEK293 cell line proteome delineates 462 complexes composed of 2,127 protein subunits. The technique identifies novel sub‐complexes and assembly intermediates of central regulatory complexes while assessing the quantitative subunit distribution across them. The quantitative protein profiles of the HEK293 dataset are available for custom exploration on https://sec-explorer.ethz.ch/.
Link to the publication in external page Molecular Systems Biology.