Intercrypt sentinel macrophages tune antibacterial NFκB responses in gut epithelial cells via TNF
A recent paper by the Hardt group (IMB) published in Journal of Experimental Medicine shows how intercrypt sentinel macrophages in the intestinal mucosa sense bacterial exposure in the lamina propia and trigger a locally confined antimicrobial NFκB response in intestinal epithelial cells.
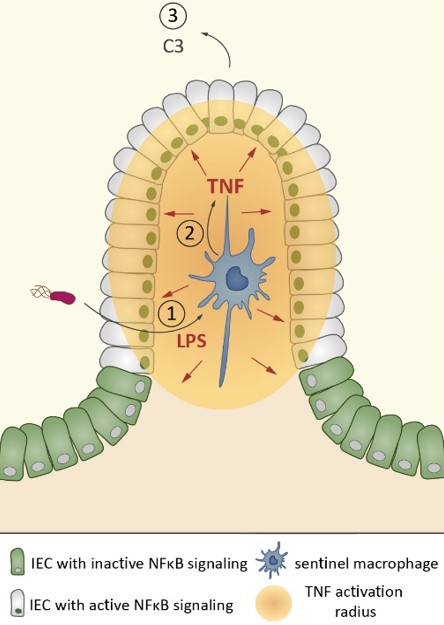
Intestinal epithelial cell (IEC) NFκB signaling regulates the balance between mucosal homeostasis and inflammation. It is not fully understood which signals tune this balance and how bacterial exposure elicits the process. Pure LPS induces epithelial NFκB activation in vivo. However, we found that in mice, IECs do not respond directly to LPS. Instead, tissue-resident lamina propria intercrypt macrophages sense LPS via TLR4 and rapidly secrete TNF to elicit epithelial NFκB signaling in their immediate neighborhood. This response pattern is relevant also during oral enteropathogen infection. The macrophage–TNF–IEC axis avoids responses to luminal microbiota LPS but enables crypt- or tissue-scale epithelial NFκB responses in proportion to the microbial threat. Thereby, intercrypt macrophages fulfill important sentinel functions as first responders to Gram-negative microbes breaching the epithelial barrier. The tunability of this crypt response allows the induction of defense mechanisms at an appropriate scale according to the localization and intensity of microbial triggers.
Link to the paper in external page Journal of Experimental Medicine