10
The human GID complex engages two independent modules for substrate recruitment
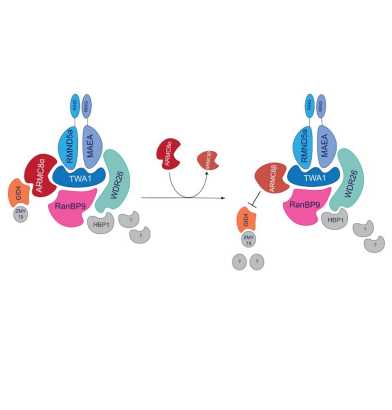
The EMBO Reports paper by the Peter group (IBC) finds that the human GID E3 ubiquitin ligase forms a tetrameric complex with two distinct substrate-recruitment modules, namely WDR26-RanBP9 and GID4-ARMC8a. Although the shorter ARMC8b isoform stably assembles into the hGID complex, it lacks the ability to recruit the GID4 substrate-receptor.
Reversible amyloids of pyruvate kinase couple metabolism and stress granule disassembly
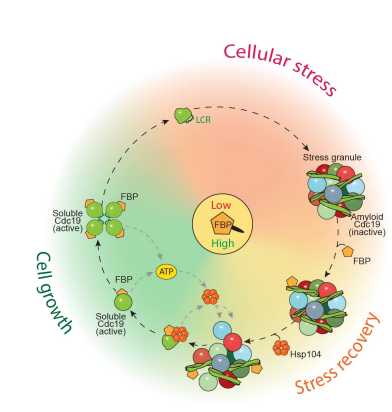
A recent "Nature Cell Biology" paper by the Peter group (IBC) in collaboration with the Sauer and Picotti groups (IMSB) elucidates a molecular mechanism that is critical for cell survival to stress, revealing how proteins can directly sense the cellular energy levels and reversibly aggregate.
Functional precision medicine prolongs survival of advanced blood cancer patients
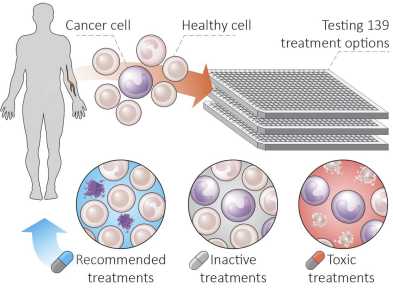
The Snijder Lab (IMSB), in collaboration with researchers from Medizinische Universität Wien and the Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences in Vienna, publish the first ever successful trial using functional drug testing for personalized treatment of patients suffering from aggressive blood cancers.
Intercrypt sentinel macrophages tune antibacterial NFκB responses in gut epithelial cells via TNF
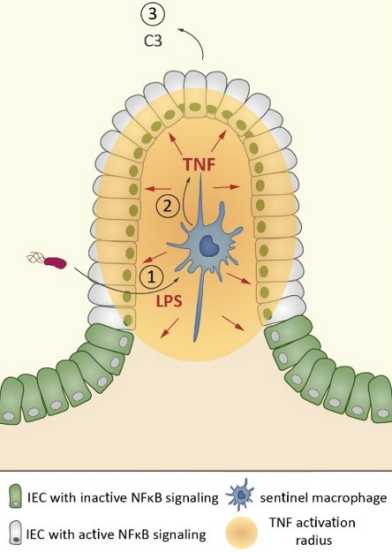
A recent paper by the Hardt group (IMB) published in Journal of Experimental Medicine shows how intercrypt sentinel macrophages in the intestinal mucosa sense bacterial exposure in the lamina propia and trigger a locally confined antimicrobial NFκB response in intestinal epithelial cells.
Extensive regulation of enzyme activity by phosphorylation in E. coli
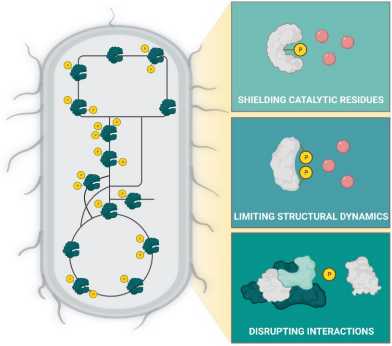
A recent "Nature Communications" paper by the Sauer group (IMSB) demonstrates surprisingly frequent metabolic phenotypes of point mutations in phosphosites of enzymes, suggesting protein phosphorylation is an underappreciated major regulation process in bacterial metabolism.