07
Starch phase transition – The ‘Domino effect’
A Science Advances article, published by the Zeeman group (IMPB) in collaboration with Prof. Coralie Bompard (University Lille), shifts a long-standing paradigm: That starch crystallization is a spontaneous physical process. The work provides compelling evidence for protein factors being involved.
Site-specific bioorthogonal protein labelling by tetrazine ligation using endogenous β-amino acid dienophiles
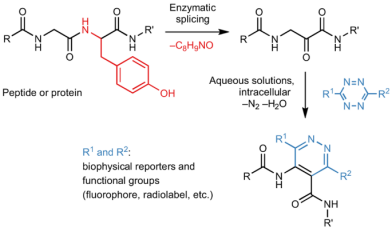
A recent "Nature Chemistry" paper by the Piel group (IMB) describes a novel bioorthogonal labelling approach. Enzymatically generated dienophiles in proteins readily react with tetrazine derivatives in physiological conditions and intracellularly.
Annette Oxenius elected EMBO member

EMBO is an organization of leading researchers that promotes excellence in the life sciences in Europe and beyond. Today it announced the election of 69 researchers, one of which is Annette Oxenius, group leader at the Institute of Microbiology at the Department of Biology. Through this lifelong honour, new EMBO Members and Associate Members are recognized for their outstanding achievements in the life sciences.
Elongated Bacterial Pili as a Versatile Alignment Medium for NMR Spectroscopy
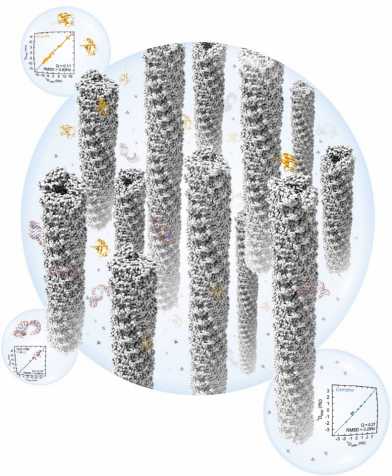
Researchers from the IMBB and the Very High Field NMR Center in Lyon introduce a novel liquid crystal that is based on filamentous type 1 pili from E. coli, resists harsh experimental conditions and allows the measurement of residual dipolar couplings for proteins, nucleic acids and small molecules by NMR.
NAC serves as a control hub for N-terminal methionine removal on the ribosome
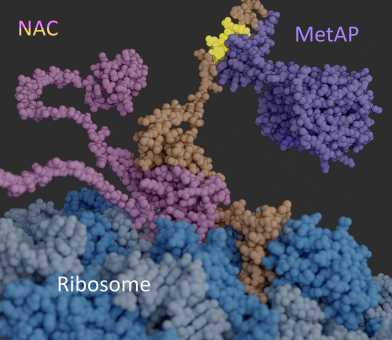
In a recent "Science" paper, the Ban (IMBB) and Deuerling labs (University of Konstanz, Germany) show that the nascent polypeptide–associated complex (NAC) controls whether the N-terminal methionine is cleaved co-translationally by methionine aminopeptidase 1 (MetAP1).