FoxM1 coordinates cell division, protein synthesis, and mitochondrial activity in β-cells
Pancreatic β-cells are essential secreting insulin to regulate glucose homeostasis. During metabolic stress they respond by increasing insulin production and secretion and proliferation to meet the increased metabolic demand. A detailed understanding of this process is important to understand the processes leading to β-cell decompensation and demise in obesity and type 2 diabetes.
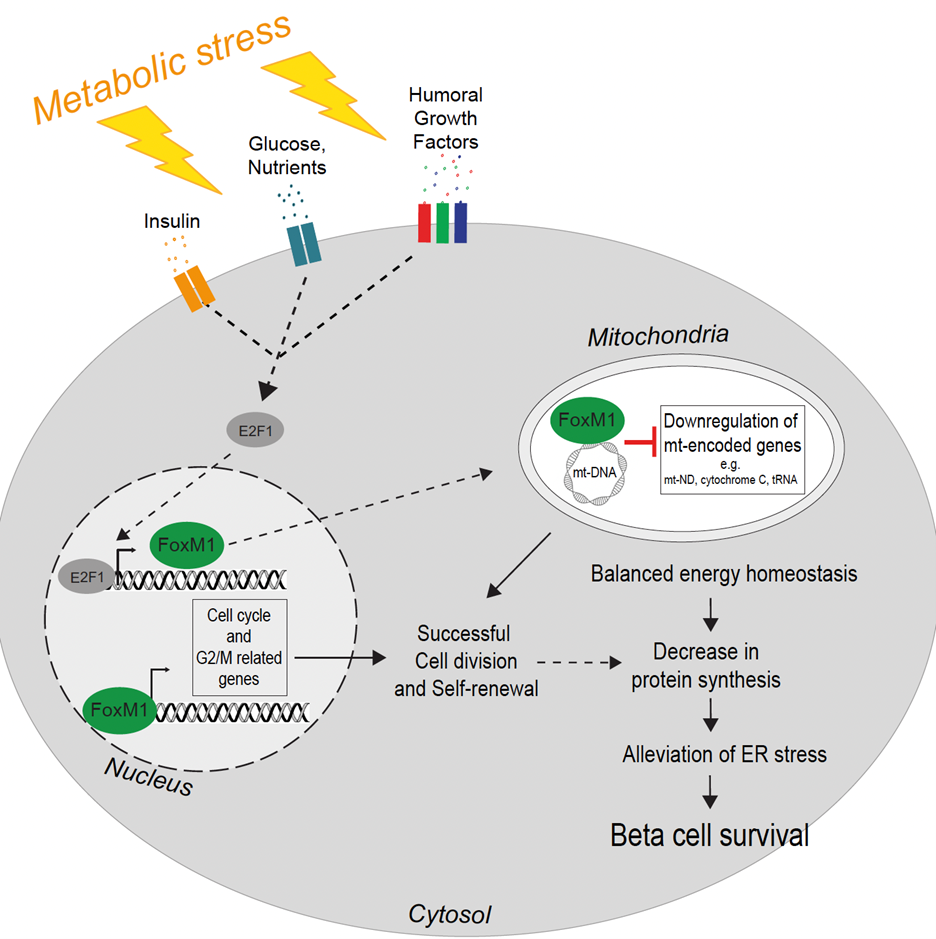
Pancreatic β-cells are essential secreting insulin to regulate glucose homeostasis. During metabolic stress they respond by increasing insulin production and secretion and proliferation to meet the increased metabolic demand. A detailed understanding of this process is important to understand the processes leading to β-cell decompensation and demise in obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Researchers at IMHS characterize β-cell responses to acute metabolic stress in vivo by employing RNA-seq, ATAC-seq, scRNA-seq, ChIP-seq and real-time imaging to decipher temporal events of chromatin remodeling and gene expression regulating the unfolded protein response (UPR), protein synthesis, mitochondrial function, and cell cycle progression.
They identified proliferation-prone pancreatic β-cells with enhanced UPR and decreased protein synthesis and insulin secretion during metabolic stress. Insulin depletion and alleviation of ER stress precede the progression of the cell cycle and ensure appropriate insulin synthesis. FoxM1 mediates this process by regulating translation and mitochondrial activity by repressing mitochondrial genes.
Link to the paper in external page "Cell Reports".