Peroxisomes are critical for a unique metabolic demand and survival of alveolar macrophages
Our lungs rely on alveolar macrophages (AMs) for health. Matsushita & Muri from the Kopf Group (IMHS) published in Cell Reports that AMs need peroxisomes to manage toxic fats, support energy metabolism, mitochondrial fitness, and safeguard lung immunity, highlighting their vital role.
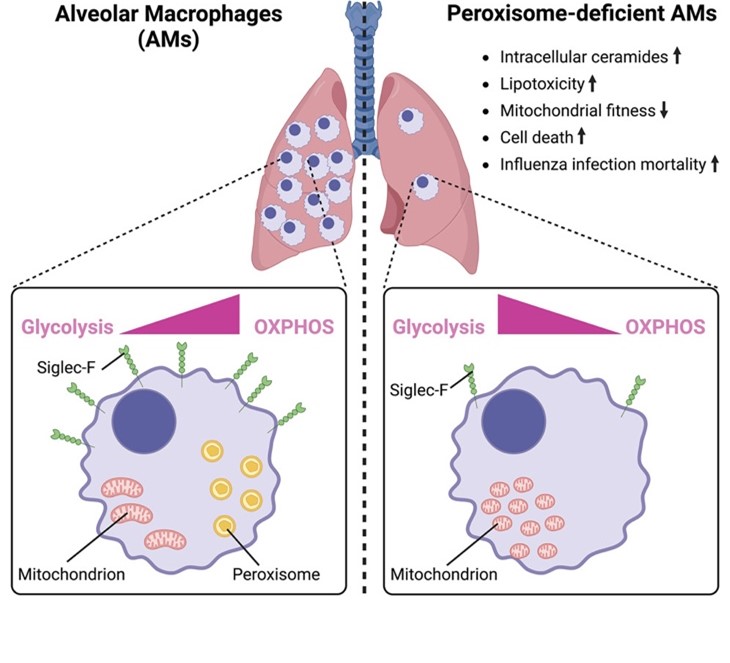
Our lungs constantly face harmful environmental particles and microbes. Specialized immune cells, known as alveolar macrophages (AMs), residing in the airspace (alveoli) where gas exchange occurs, play a crucial role in clearing airborne particulate matter and pathogens. This study demonstrates that AM rely on peroxisomes, a type of cellular organelle, for their development and maintenance. In contrast, resident macrophages in other tissues get along without peroxisomes.
In AMs, peroxisomes are essential for breaking down toxic long-chain fatty acids and ensuring cell survival. In their absence, AMs lose their ability to meet their unique energetic needs, resulting in metabolic imbalance and accumulation of damaged mitochondria, which ultimately weakens lung immunity. Our findings reveal the vital role of peroxisomes in maintaining the energy balance, mitochondrial fitness, and survival of AM, highlighting their key function in protecting lung health and immune defense.
Link to the paper in external page "Cell Reports".