Structure of the microtubule-anchoring factor NEDD1 bound to the γ-tubulin ring complex
In a recent article in the “Journal of Cell Biology”, the Wieczorek Group reports cryo-EM structures that reveal how the γ-tubulin ring complex (γ-TuRC)-associated protein NEDD1 anchors the complex at microtubule-organizing centers without interfering with microtubule nucleation.
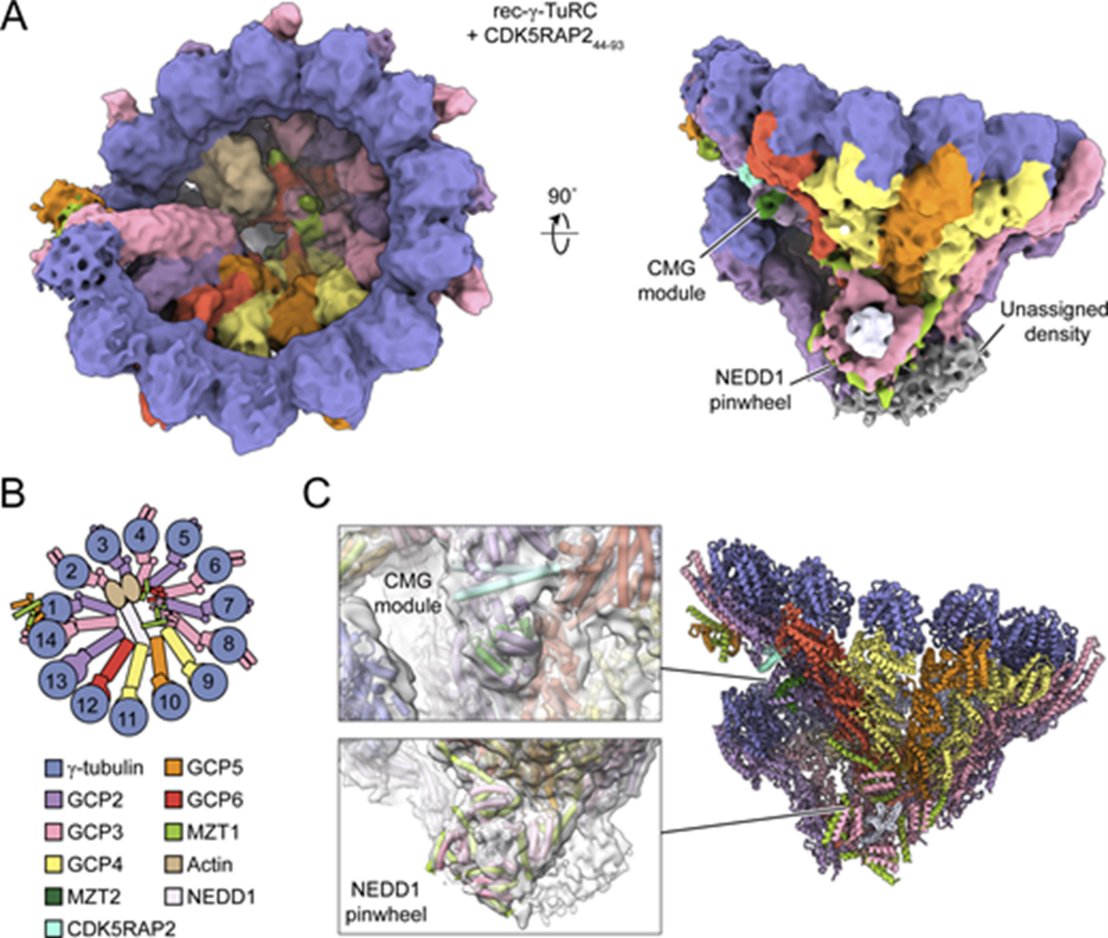
Microtubules are essential cytoskeletal structures found in all eukaryotic cells. Microtubules are nucleated by the γ-TuRC, a multisubunit protein complex that provides a template for the 13 protofilament microtubule and remains bound to filament minus ends as a stabilizing cap. The γ-TuRC is recruited to a variety of microtubule-organizing centers, including centrosomes and spindle microtubules, by a protein called NEDD1, but the molecular basis of this recruitment is not understood.
Researchers at IMBB in collaboration with The Rockefeller University determined cryo-EM structures of the human γ-TuRC in complex with NEDD1. The structures reveal that NEDD1’s C terminus forms an α-helical tetramer that docks onto the bottom of the γ-TuRC without inducing major conformational changes in the complex. The NEDD1-bound γ-TuRC structure is compatible with the binding of activating factors such as CDK5RAP2 that lead to γ-tubulin ring closure, a key rate-limiting step in microtubule nucleation.
The study shows how NEDD1 acts as a microtubule minus end anchoring factor at centrosomes and sheds light on the growing repertoire of γ-TuRC-regulating proteins. The structures also pave the way to understanding other functions of NEDD1, such as in linking the γ-TuRC to the Augmin complex in microtubule branch structures in mitotic spindles in a phosphorylation-dependent manner.
Link to the paper in the external page "Journal of Cell Biology "