09
Genome-based discovery and total synthesis of janustatins, potent cytotoxins from a plant-associated bacterium
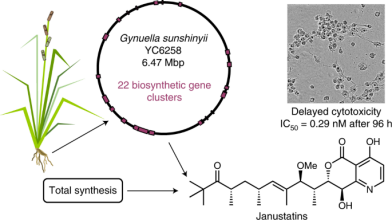
A combination of genome mining, analytical and computational chemistry, total synthesis, molecular biology enabled the discovery of novel potent cytotoxins, janustatins. This collaborative effort of the Piel and Oxenius groups (D-BIOL, Institute of Microbiology), with the Carreira group (D-CHAB, Laboratory of Organic Chemistry) as well as Japanese and US researchers was recently published in Nature Chemistry.
Artificial intelligence improves drug testing in patient samples for personalised medicine

A recent "Blood Cancer Discovery" paper by the Snijder group (IMSB) in collaboration with the Medical University of Vienna, CeMM, and Exscientia shows that deep learning of cell morphologies improves the clinical treatment recommendations obtained by drug screening in patient samples.
Punching a hole in the nuclear membrane
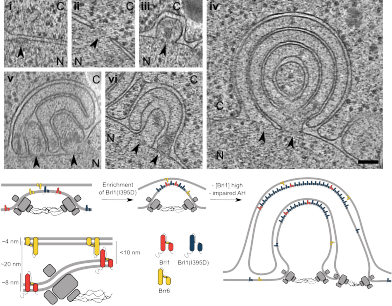
A recent eLife paper from the Weis group, in collaboration with the Medalia, Onischenko and Antonin labs, suggests a role for the protein Brl1 in the enigmatic membrane fusion event that leads to a functional nucleocytoplasmic transport channel during nuclear pore complex biogenesis.
Synthetic methylotrophy for methanol biotransformation
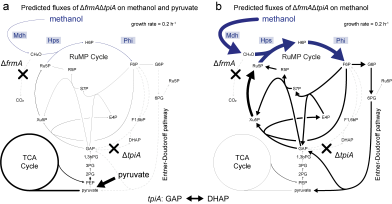
The generation and conversion of renewable methanol, produced from the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide or methane, is a promising avenue for reducing greenhouse gases and replacing fossil fuels. The Vorholt lab has converted the biotech strain E. coli into an organism that feeds on methanol, laying the foundation for its sustainable valorization in the future.