04
Transport of CLCA2 to the nucleus by extracellular vesicles controls keratinocyte survival and migration
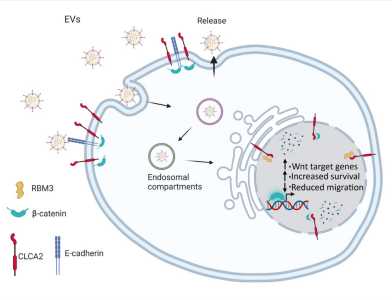
A recent "Journal of Extracellular Vesicles" paper by the Werner group (IMHS) identified an unexpected nuclear transport mechanism of the stress-regulated transmembrane protein CLCA2 by extracellular vesicles (EVs). The presence of CLCA2 in the nucleus is required for the regulation of key cellular functions in skin keratinocytes.
Assembly platform FimD ensures most stable quaternary structure formation of type 1 pili
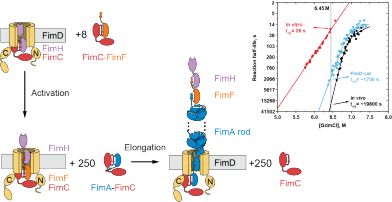
In a "Nature Communications" article, the Glockshuber (IMBB), Hospenthal (IMBB), Waksman (UCL and Birkbeck, UK), Meier (LPC, D-CHAB) and Wiegand (RWTH Aachen University, Germany) groups, show that the assembly platform FimD is required to assemble the most stable quaternary structure of type 1 pili.
Buffer and pH Strongly Affect the Phase Separation of SARS-CoV-2 N Protein
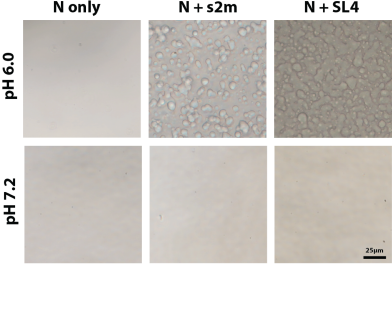
The Allain lab (IBC) in a "Molecular Biology of the Cell" paper reported that the phase separation of the SARS-CoV-2 N protein strongly depends on the chosen buffer and pH. For example, the protonation of a single histidine side chain makes the difference if the protein phase separates or not.
Evolution-guided engineering of trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthases
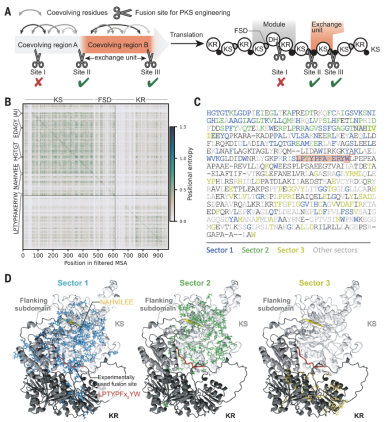
The publication in Science by the Piel group (IMB) in collaboration with the Piechulla (University of Rostock) and Walker group (Vanderbilt University) reports a method that permits the construction of tailored bacterial biosynthetic pathways for structurally complex polyketide metabolites, based on ways how modular megaenzymes evolve naturally.