09
A primary cell wall cellulose‐dependent defense mechanism against vascular pathogens revealed by time‐resolved dual‐transcriptomic
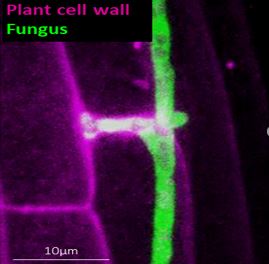
How do plants coordinate growth and defense against pathogens? A recent "BMC Biology" paper led by Alex Menna, Susanne Dora, and Gloria Sancho-Andrés from the Sánchez-Rodríguez group (IMPB) presents a novel molecular mechanism for how the dynamic regulation of cellulose synthesis during root vascular pathogens infection directly influences plant resistance to microbes.
A tango with four: Evolutionary modification of crossover interference enables stable autopolyploidy
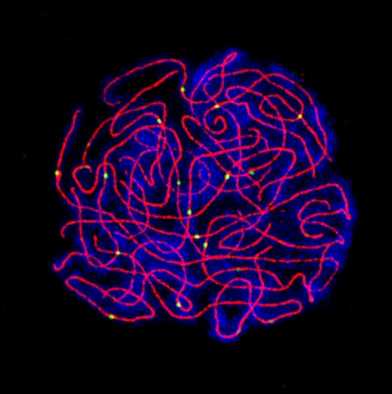
How do you do meiosis with four copies of every chromosome instead of two? A recent "Current Biology" paper by the Bomblies group (IMPB) with collaborators Nancy Kleckner (Harvard) and others, presents a new model suggesting increased crossover interference is key in stabilizing polyploid meiosis.
Structures of ABCB4 provide insight into phosphatidylcholine translocation
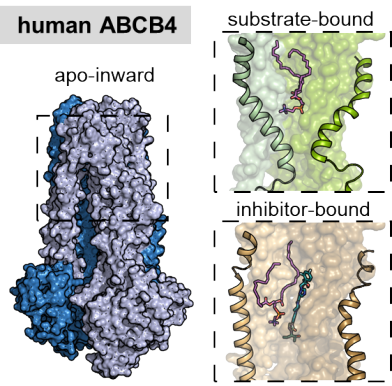
A paper recently published in “PNAS” by the Locher group (IMBB) demonstrates how human phosphatidylcholine transporter, ABCB4, recruits substrate lipid from the lipid bilayer and translocates it into bile canaliculi, and how this process is inhibited by the antifungal drug posaconazole.
Processing of FUBI-eS30 is required for 40S ribosome maturation and depends on USP36
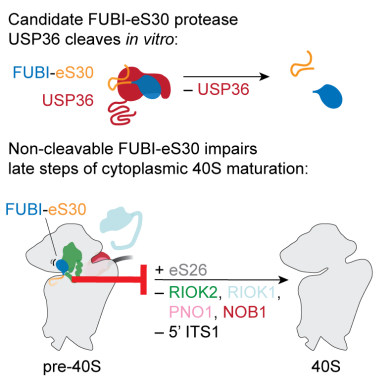
The ubiquitin-like protein FUBI and the ribosomal protein eS30 are synthesized as one polypeptide chain. A recent eLife publication by the Kutay group discovered that USP36 is involved in endoproteolytic cleavage of the fusion protein; a reaction licensing efficient final maturation of 40S subunits.