11
Plant protection potential in the leaf microbiota of Arabidopsis
Plants can be protected from diseases by their resident bacteria. In a Nature Microbiology paper, the Vorholt lab systematically analyzed over 200 Arabidopsis leaf bacteria for their protection against a common pathogen and identified complementary mechanisms of protection at play.
The Atg1 kinase complex orchestrates spatial and temporal control of autophagosome formation
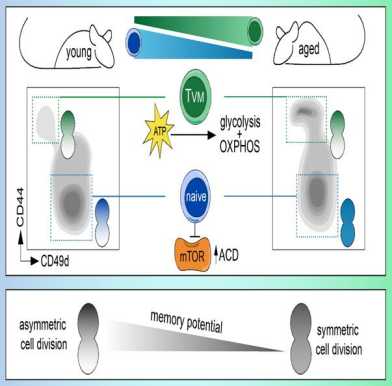
A recent paper by the Peter and Aebersold groups reports that the Atg1 kinase complex functions at multiple levels during autophagy. Upon autophagy induction, lipidated Atg8 activates the Atg1 kinase, which in turn phosphorylates Atg13 triggers its dissociation. Active Atg1 then travels along the growing autophagosome, where it inhibits two enzymes involved in Atg8 lipidation.
Structures of Pup in complex with depupylase Dop reveal the mechanism of catalytic Pi formation
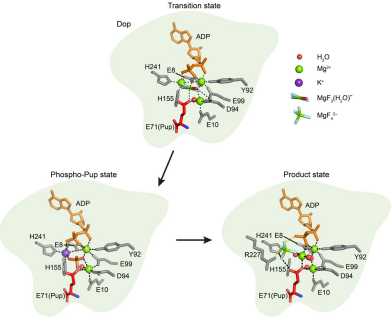
Mycobacteria mark proteins by pupylation, a process akin to ubiquitination. A pair of related enzymes catalyze attachment and removal of Pup. A Nature Communications article by the Weber-Ban lab reveals how depupylase Dop generates the catalytic phosphate that enables Dop to cleave the bond between Pup and targets.
NabFab: A nanobody-binding Fab for fiducial-assisted cryo-EM studies of membrane proteins
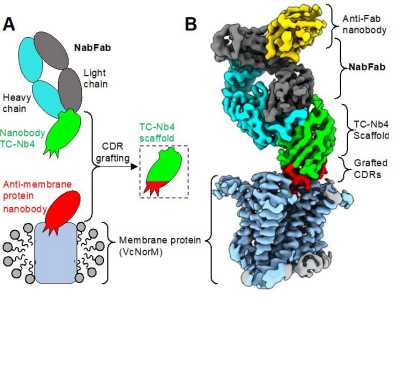
Small integral membrane proteins comprise a large portion of drug targets in humans. These proteins are often resistant to structure determination. A recent "PNAS" by the Locher group (IMBB) in collaboration with the Kossiakoff Group (University of Chicago) describes a widely applicable solution.
Structure and regulation of the microtubule plus-end tracking protein Kar9
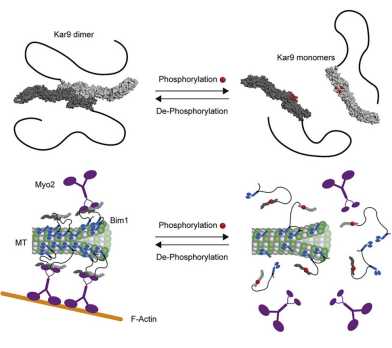
In Structure, the Barral (IBC) and Steinmetz (PSI) labs provide structural insights in the microtubule-tracking protein Kar9, revealing how regulation of its dimerization orients the mitotic spindle in dividing cells. This study uncovers Kar9’s relationships to metazoan MACF/ACF7/Shot and PRC1.