04
Unlocking the Mystery of Microtubule Growth: The Intricate Dance of Kip2 and Bik1
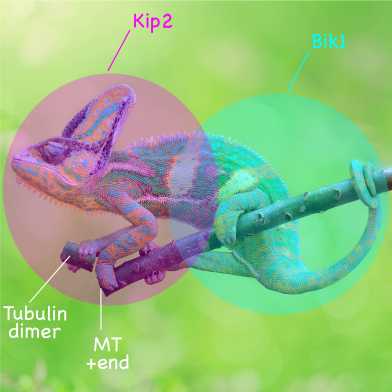
In a multidisciplinary study newly published in the Journal of Cell Biology, the Barral group (ETHZ, D-BIOL/IBC) together with the Steinmetz group (PSI), the Stelling group (ETHZ, D-BSSE) and the Liakopoulos lab (CNRS, Montpellier) sheds light on how the motor domain of the kinesin protein Kip2 collaborates with the microtubule plus-end-binding protein Bik1, to moonlight as a microtubule polymerase.
ClpC2 protects an essential mycobacterial degradation pathway against cyclomarin A toxicity
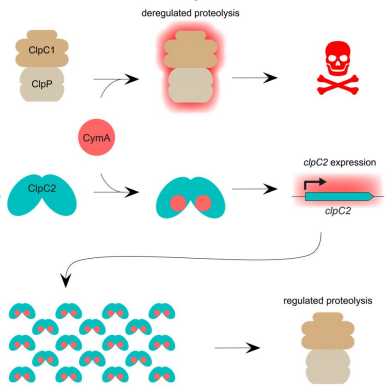
In a recent paper published in “Communications Biology”, the Weber-Ban group (IMBB) demonstrates a role for a ClpC1 partial homologue in helping to protect an essential protein degradation pathway against the antibiotic Cyclomarin A in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Understanding Randomness on a Molecular Level: A Diagnostic Tool
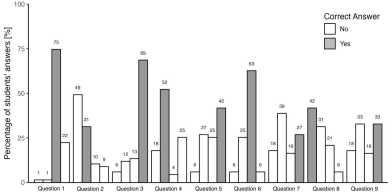
In a recent “CBE–Life Science Education” paper the Center for Active Learning (D-BIOL) and the Kapur lab (D-GESS) present a novel tool and its use to test students’ grasp of molecular randomness, revealing the dimensions and the evolution of conceptual understanding with growing expertise.
Structural basis of calmodulin modulation of the rod cyclic nucleotide-gated channel
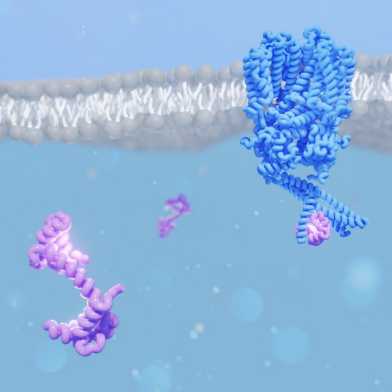
A "PNAS" paper coordinated by Jacopo Marino with contributions from the Schertler, Korkhov, Leitner, Picotti & Kaupp groups (PSI, IMBB, IMSB and Uni Bonn) reports the structure of the rod cyclic nucleotide-gated channel in complex with calmodulin. The combination of cryo-EM & structural proteomics explains crucial steps in visual signal transduction.
Mesenchyme-derived VLK controls lung organogenesis by altering the matrisome
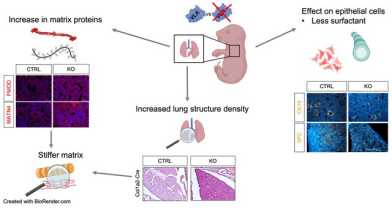
A "Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences" paper by the Bordoli group (Werner lab, IMHS) sheds light onto the role of vertebrate lonesome kinase (VLK) in lung organogenesis. Mesenchyme-derived VLK regulates matrix dynamics and ultimately alveolar epithelial cell differentiation by altering the matrix proteome.