02
Nanobody-drug conjugates hijack the human vitamin B12 uptake route
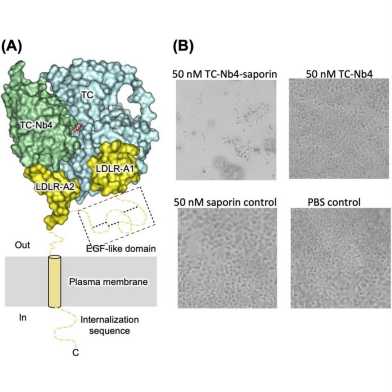
A major challenge in cancer therapy is selectively targeting cancer cells over healthy ones. A recent study by the Locher group (IMBB) describes the development of camelid single-domain antibodies (nanobodies) that selectively deliver cargo to cells by hijacking the cellular vitamin B12 uptake pathway which is high in demand in cancer cells.
Microbial community assembly is structured by metabolic cross-feeding networks
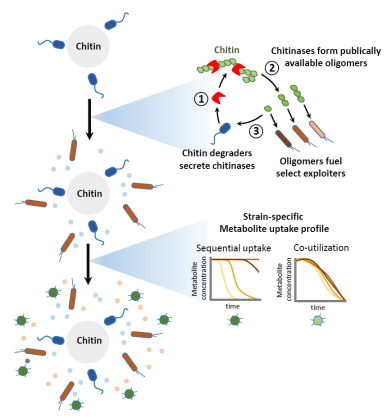
A recent “Science Advances” paper by the Sauer group (IMSB) uses a model chitin degrading community to demonstrate how metabolic cross-feeding networks are formed by specialized chitin degraders, and how these networks structure the downstream assembly of metabolically diverse populations.
A quiet evolutionary response to cellular challenges
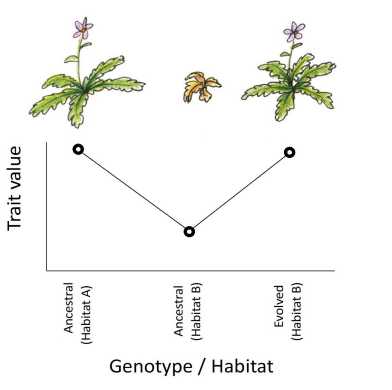
In studying evolution, we often focus on showy traits. But a recent essay by Kirsten Bomblies (IMPB, DBIOL) highlights that “invisible” adjustments that maintain cellular functions in novel contexts are an important force in evolution and can help interpret signatures of selection in genome scans.
CRISPRi meets metabolomics: a platform for rapid functional annotation of compound libraries
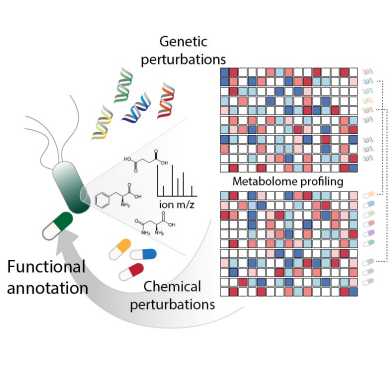
By linking drug-induced metabolic changes to CRISPR interference of essential genes, the Zampieri group (IMSB) in collaboration with the Picotti (IMSB), Berney (Einstein) and Jenal (Biozentrum) groups, propose a new strategy for comprehensive high-throughput analysis of drug functionality, from bacteria to human cell lines.
Genome-wide screen for human 60S biogenesis factors reveals role of polyamine metabolism
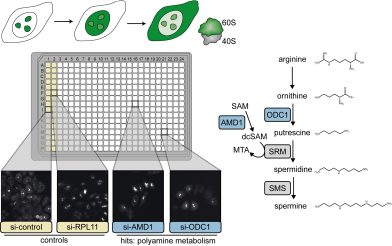
Human cells use large parts of their proteome for ribosome synthesis. In a manuscript published in NAR, the Kutay group exploited a genome-wide screening approach to identify factors required for 60S subunit biogenesis, which revealed an unexpected role of polyamine metabolism in 60S maturation.