Cancer-associated fibroblast classification in single-cell and spatial proteomics data
A recent "Nature Communications" paper by the Bodenmiller group (IMHS) suggests a novel classification system for cancer-associated fibroblasts for single-cell and spatial proteomics data for the systematic study of this cell type.
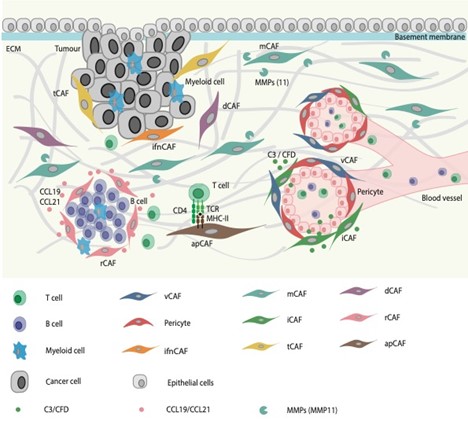
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) are a highly heterogeneous cell type found in tumours. Distinct CAF subsets have been found to make vital contributions to tumour progression as well as patient prognosis. However, comparability of CAF subtypes between different studies remains difficult, especially due to the lack of a general CAF classification system.
Analysing CAF heterogeneity at the single-cell level, researchers of the Bodenmiller group at the IMHS were able to develop a classification system for CAFs. Using both transcriptomic and spatial proteomics data from human breast cancer specimen, they identified nine different CAF types that they annotated functionally. They were further able to validate their defined CAF types in single-cell data from different cancer types, suggesting the general applicability of their classification system. Finally, their use of patient matched spatial single-cell analysis revealed the different spatial distribution patterns of the different CAF types.
The proposed classification system of this study can be used for the comparison of CAF types across cancer types and studies and inform studies investigating the functional roles of the different subtypes in cancer, which might ultimately result in novel targets for cancer therapeutics in the future.
Link to the paper in external page "Nature Communications".
Comments
No comments yet